Site search:
-
What’s new?
Energy for London Tags
Brent Buildings Camden Carbon Emissions CHP Cities Climate Adaptation Community Heating Community Initiatives Croydon Data DECC Decentralised Energy Distribution ECO Energy Costs Energy Efficiency Enfield FIT Fuel Poverty Funding Green Deal Hackney Haringey Housing Islington Lambeth Library Local Authorities Mayor Newham Ofgem Olympics Photovoltaics Planning RE:FIT RE:NEW Renewable Energy Retrofit Southwark Tower Hamlets Transport Waltham Forest Waste WestminsterEnergy Archives:
- February 2021 (1)
- January 2021 (15)
- December 2020 (15)
- November 2020 (9)
- October 2020 (3)
- August 2020 (5)
- July 2020 (3)
- June 2020 (4)
- April 2020 (10)
- March 2020 (5)
- February 2020 (2)
- January 2020 (3)
- October 2019 (1)
- September 2019 (4)
- August 2019 (2)
- July 2019 (1)
- August 2018 (1)
- November 2016 (8)
- October 2016 (8)
- September 2016 (2)
- August 2016 (8)
- July 2016 (14)
- April 2016 (12)
- March 2016 (16)
- February 2016 (8)
- January 2016 (4)
- December 2015 (1)
- November 2015 (1)
- October 2015 (16)
- September 2015 (3)
- June 2015 (1)
- May 2015 (1)
- April 2015 (1)
- March 2015 (1)
- February 2015 (1)
- January 2015 (1)
- December 2014 (18)
- November 2014 (4)
- August 2014 (8)
- July 2014 (7)
- June 2014 (25)
- May 2014 (8)
- April 2014 (4)
- March 2014 (12)
- February 2014 (7)
- January 2014 (13)
- December 2013 (11)
- November 2013 (15)
- October 2013 (15)
- September 2013 (18)
- August 2013 (5)
- July 2013 (20)
- June 2013 (33)
- May 2013 (8)
- April 2013 (16)
- March 2013 (25)
- February 2013 (14)
- January 2013 (20)
- December 2012 (23)
- November 2012 (23)
- October 2012 (25)
- September 2012 (14)
- July 2012 (12)
- June 2012 (43)
- May 2012 (20)
- April 2012 (8)
- March 2012 (40)
- February 2012 (39)
- January 2012 (40)
- December 2011 (22)
- November 2011 (40)
- October 2011 (33)
- September 2011 (48)
- August 2011 (40)
- July 2011 (58)
- June 2011 (41)
- May 2011 (80)
- April 2011 (38)
- March 2011 (33)
- February 2011 (25)
- January 2011 (24)
- December 2010 (3)
- November 2010 (7)
- October 2010 (6)
- September 2010 (7)
- August 2010 (1)
- July 2010 (2)
- June 2010 (4)
- May 2010 (1)
- March 2010 (3)
- February 2010 (3)
- December 2009 (5)
- November 2009 (2)
- October 2009 (3)
- July 2009 (3)
- June 2009 (1)
- April 2009 (1)
- March 2009 (1)
- February 2009 (1)
- January 2009 (1)
- December 2008 (2)
- October 2008 (1)
- September 2008 (1)
- July 2008 (1)
- March 2008 (2)
- January 2008 (2)
- October 2007 (1)
- September 2007 (3)
- July 2007 (1)
- March 2007 (1)
- February 2007 (3)
- November 2006 (3)
- August 2006 (1)
- February 2006 (1)
- May 2005 (1)
- February 2004 (1)
Decentralised Energy
Fuel Cells in London
November 2013: The Guardian highlighted in a recent story that the London HQ of Al Gore’s business is to be based in a new office development on Regent Street which has included a wide array of onsite energy measures installed including a gas-powered fuel cell.
“Climate campaigner and former US vice-president Gore said the £400m Quadrant 3 redevelopment showed a “sophisticated commitment to sustainability”. The headquarters of his sustainable investment company, Generation Investment Management, will be sited in the new buildings.
“The cell was developed by US company FuelCell Energy. It will emit 38% less carbon dioxide than using electricity from the grid and heat from gas-fired boilers, according to the crown estate, which says 350 tonnes of carbon dioxide emissions will be saved per year. Unlike fossil-fuel-burning power plants, the fuel cell produces power with virtually no nitrogen oxide (NOx), sulphur dioxide (SOx) or particulate matter (PM) pollution.
The new plant forms part of the central energy system that serves 500,000 sq ft of offices, shops, flats, restaurants and hotels in the Quadrant development.” Read the full Guardian story here.
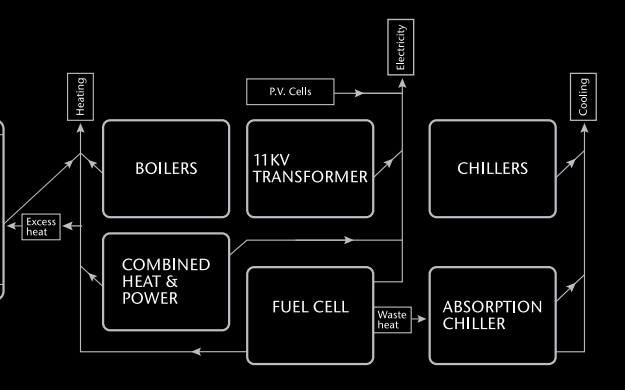
Further detail on the installation of the fuel cell can be read here – which has been undertaken by Edinburgh based Logan Energy. The Quadrant 3 development has a number of other onsite energy measures installed (including a Combined Cooling Heat & Power plant, thermal stores and photovoltaics – see diagram below), as set out in the property brochure.
Another new London development to include fuel cell technology is that on 20 Fenchurch Street (more commonly known as the ‘Walkie Talkie’ building) which has installed a 300 kWe fuel cell, details of which can be read here and here.
Transport for London installed a fuel cell CHP in their Palestra building in Southwark back in 2010, details of which – including a video presentation – can be seen here and here.
Posted in Decentralised Energy, News
Tagged CHP, City of London, Fuel Cells, Southwark, Westminster
Leave a comment
Developing Heat Networks in London
November 2013: At the BRE’s recent event Developing heat networks in the UK three presentations were delivered on developments in London – links to which follow below:
Bunhill Heat and Power – Charlotte Large, Decentralised Energy Programme Manager, Islington Council
Identifying secondary heat sources for future sustainable heat networks – Peter North, Senior Manager – Programme Delivery (Sustainable Energy), GLA
The third presentation by Ian Smith, Head of Sustainable Services, Southwark Council, on London’s first energy from waste district heating network, can be found here.
Posted in Decentralised Energy, News
Tagged CHP, Community Heating, Decentralised Energy, Islington, SELCHP, Southwark, Waste
Leave a comment
Designing with data: shaping our future cities
 November 2013: A new report undertaken by ARUP for RIBA sets out that we are now at the “Dawn of a ‘smart era [where the] vast quantities of data we produce is set to revolutionise the way we design and build our cities”. A series of case studies are set out in ‘Designing with data: shaping our future cities‘ which includes the London Heat Map:
November 2013: A new report undertaken by ARUP for RIBA sets out that we are now at the “Dawn of a ‘smart era [where the] vast quantities of data we produce is set to revolutionise the way we design and build our cities”. A series of case studies are set out in ‘Designing with data: shaping our future cities‘ which includes the London Heat Map:
“One of the key benefits of adopting a smart approach to data is the ability to see lots of datasets in context with each other, and to detect temporal and spatial patterns. This transparency saves time and cost by reducing the time needed to find and process key data. The London Heat Map is a case in point. The interactive tool developed by the Greater London Authority (GLA) allows people to identify opportunities for Decentralised Energy projects in London, such as Combined Heat and Power (CHP) or district heating networks. Public organisations, property developers, social landlords or investors can also use it to view spatial information that can help them identify and develop Distributed Energy opportunities, such as data on: major energy consumers, fuel consumption and carbon emissions,energy supply plants, community heating networks,and heat density. The London Heat Map will evolve overtime alongside the Decentralised Energy for London programme and become more useful and sophisticated as boroughs and other stakeholders start inputting more energy data into the map.”
The report goes on to quote Alan Shingler, Partner, Head of Sustainability, Sheppard Robson who states “smart data could help test the impact of likely building fabric improvements through the Government’s Green Deal or regeneration schemes, to show how the GLA’s Heat Map would adjust to these variables. The data could also be used to model the impact of new renewable energy generation and future development on the map. This would enable the creation of a resilient low carbon transition plan for London that would take into account a range of considerations….where Combined Heat and Power (CHP) is proposed, heat could be more freely shared with neighbouring residential developments, schools, or public buildings with a relatively high heat load.“
Three recommendations are made in the report including one Energy for London strongly supports which is the greater ‘Digitisation the of the planning process’ where “Government should scope how it can standardise the digitisation of all information submitted for planning, and of standardising design data collection across local authorities. This public data should be open to unleash economic growth; and local authorities should be encouraged to use open data to inform local planning strategies.”
Posted in Decentralised Energy, News
Tagged Decentralised Energy, Heat Maps, London Heat Map, Planning
Leave a comment
GLA responds to Heat Enquiry
November 2013: The House of Commons Energy and Climate Change Select Committee is currently undertaking an enquiry into Heat. The terms of reference to the enquiry states that “so far much of government’s energy policy focus has been on low-carbon electricity generation (in particular, the Energy Bill, which aims to reform the electricity market). Yet heat is responsible for 46% of UK energy use, approximately a third of UK greenhouse gas emissions, and is a major cost in both the domestic and non-domestic sectors.”
The Greater London Authority (GLA) has submitted written evidence to the Committee outlining the significant decentralised energy programme underway in the capital. The evidence sets out a number of interesting points related to the wider scale deployment of heat networks as well as recommendations to Government in terms of its policies to promote decentralised generation. These include:
- The Mayor welcomes the Committee’s scrutiny of this often over-looked area of energy policy
- There are “inconsistencies in government’s energy policy and regulatory regime that are preventing heat generation and distribution in cities” which “…distort the market for heat by providing external financial support for some technologies, while largely ignoring heat networks“.
- Heat network deployment at the scale envisaged for London represents a significant infrastructural challenge, requiring approximately 3,600km of heat networks to be constructed by 2030 and equates to an investment opportunity of approximately £6bn
- Whilst district heating schemes can qualify for funding under ECO, the current two year target as well as uncertainty regarding longer-term target discourage energy suppliers from investing in these schemes. Government should consider setting longer term targets for the next phases of ECO, or provide guidance on how investment in district heating schemes can contribute to current or future targets
- We estimate that London housing development will generate at the very least £25m per annum under the proposed Allowable Solutions regime – by far the greatest amount of any region. Yet, because measures are likely to be cheaper outside London, London businesses and households will again be subsidising other regions and receiving less investment into low carbon, heating bill reducing measures. In addition, as Allowable Solutions investment is likely to lever ECO investment, there is a risk that the proposed scheme will exacerbate the imbalance in ECO investment away from London.
The Committee’s evidence gathering process continues in November – more of which can be found here.
Energy & Climate Questions to the Mayor
October 2013: This month the Mayor has been asked questions in relation to:
Climate change leadership; London’s successful ‘green economy”;
potential for wind energy in London; the human contribution to climate change; Nissan Electric taxis‘; emissions from electric vehicles; promoting community energy through planning; Mayor’s briefing to the House of Lords on the Energy Bill; Mayoral visits to the Dagenham wind power project; RE:NEW programme advice on supplier switching; supplier switching advice; Nuclear power and London; bills savings achieved by households under RE:NEW; the Mayor’s energy advisor’s visit to New York; the Mayor’s energy advisor’s visit to Rio de Janeiro; the Mayor’s view on wind farms; London Energy Efficiency Fund (LEEF) Advisory Committee papers; nuclear power value to Londoners; roll-over energy contracts for SMEs; CO2 savings achieved under RE:NEW; the Mayor’s energy advisor’s visit to San Francisco; the Mayor’s view on MASDAR’s investment in the London Array; the Mayor’s view on shale gas; investment opportunities for London through financing wind power projects; hosting a London ‘Climate Week‘; RE:NEW advice supplier switching; renewable electricity supply to the Tube; SOURCE London charging points; London’s need for more electricity substations; completion of Affordable Warmth and Health Action Plan; applications to the London Schools Hydrogen Challenge; budget allocated to the Mayor’s new Affordable Warmth and Health Action Plan; the Mayor’s new Affordable Warmth and Health Action Plan; Londoners supported through the Mayor’s Know Your Rights helpline; GLA officers working on the new Affordable Warmth and Health Action Plan; RE:NEW report backs; Benefit Entitlement Checks (BECs) under RE:NEW; carbon offsets for flights; key activities in the Mayor’s new Affordable Warmth and Health Action Plan; private sector funding leveraged by RE:NEW; targets under the Affordable Warmth and Health Action Plan; community level responses to heatwaves; disseminating research undertaken to date on how to cope with heatwaves and the health impacts of cold homes.
Previous months questions to the Mayor can be found here.
Licence Lite Update
October 2013: There has been little news recently on progress being made for the first ‘license lite’ license to be awarded – however – discussions do continue and below some recent references to the initiative are gathered together.
First, DECC’s Community Energy – Call for Evidence paper published in June 2013 covered the issue stating:
“96. Community renewable electricity projects typically sell their electricity through Power Purchase Agreements (PPAs), whereby an energy supply company agrees to buy electricity from a generator over a fixed period of time at a fixed rate. For community electricity generators it can be difficult to negotiate with large energy supply companies. Aggregators such as Smartest Energy have in the past helped community groups overcome this hurdle. We also recognise that the move from the Renewables Obligation to the Contracts for Difference (CfDs) is a significant one and that the structure of PPAs will need to change, to reflect the changes to the risk profile and the structure of CfDs. The Government has initiated a process to support the market in preparing for the CfD in order to speed this transition and reduce costs.
97. Another route to market for community-generated electricity is Licence Lite, a new form of electricity supply licence, which was proposed by Ofgem in February 2009. The purpose of the licence is to enable smaller scale electricity generators to overcome the costs, risks and complexities of operating in the electricity supply market. If successfully implemented, it will enable them to supply electricity into the retail electricity market and earn a higher market rate than at present for the power they produce.
98. Although no Licence Lite has yet been granted, initial applications have recently been made, including by the Mayor of London, through the Greater London Authority. We hope this will help resolve some of the issues around selling community-generated electricity, and we will be keen to see what evidence comes out of these cases.“
And two recent workshops also provided some information on the background to Licence Lite. At Ofgem’s community energy workshop held in September, Ofgem officials provided a short presentation on the basic benefits of being ‘License Lite’. And law firm Nabarro – who have undertaken significant work in this area for the GLA – held an event in July with a strong focus on licence lite where a helpful presentation was provided by the GLA providing information of their work to date and anticipated further actions. Some previous posts also go into further detail.
London’s secondary heat resource
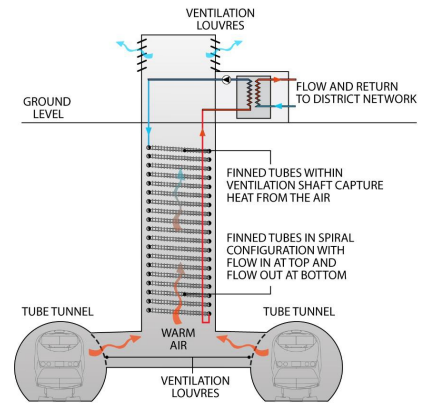
October 2013: The GLA commissioned a detailed report earlier this year exploring opportunities in London to use high volumes of typically lower-temperature waste heat. Further details on this study – London’s Zero Carbon Energy Resource – can be downloaded here. And a recent presentation made at BRE’s ‘Developing heat networks in the UK ‘ also provides a good summary of some of the findings.
Heat is generated in London’s tube network as a result of trains braking, underground lighting and from passengers. This heat is rejected through ventilated shafts at strategic positions along the network at temperatures ranging typically from 12-29 degrees.
Most secondary heat sources need upgrading to higher temperatures to be useable in heat networks – this requires heat pumps. The minimum suitable temperatures for district heating is 55 degrees. Download the presentation ‘Secondary Heat – London’s Zero Carbon Energy Resource‘ here.
London’s ‘first EfW DH network’
October 2013: A presentation made at BRE’s recent ‘Developing heat networks in the UK ‘ provides a little background – and a few images – behind the new Southwark district energy network taking waste heat from the SELCHP energy from waste (EfW) plant and directing to five nearby housing estates -presentation here (and directly here). Further information on the following post here.
Posted in Decentralised Energy, News
Tagged Community Heating, Decentralised Energy, SELCHP, Southwark
Leave a comment
Elephant & Castle plans to be ‘Climate Positive’
October 2013: London SE1 community website recently reported that “Lend Lease’s Elephant & Castle programme has been formally recognised by C40 Cities Climate Leadership to become the third project of 18 globally to reach ‘participant’ status.
The ‘climate positive participant’ rating is conferred by sustainability experts acting on behalf of C40’s Climate Positive Development Programme in partnership with the Clinton Climate Initiative.
To achieve this status, Elephant & Castle developers have submitted a roadmap which demonstrates that the scheme is set to be climate positive by 2020.”
Further information on the Elephant and Castle regeneration website states construction started last month on “the first 500 new homes …[which] will be some of the most sustainable, energy efficient and occupier-friendly places to live in Britain.” Amongst the ‘green’ initiatives to be incorporated in to what is one of the largest regeneration sites in Europe will be an ” on-site combined heat and energy centre [which] will not only provide heat and power to the homes and shops, it will also act as an interactive community and educational centre for the public.”
Some further background to this scheme and its carbon-reduction plans can be read in an earlier post here.
Posted in Decentralised Energy, News
Tagged CHP, Community Heating, Decentralised Energy, Planning, Southwark
Leave a comment
“The Rise of Distributed Generation”
October 2013: PWC’s latest annual energy and utilities survey – ‘Energy Transformation: The impact on the power sector business model‘ is proving quite a stir as a result of its findings on the future of the electricity generation sector. An incredible “82% see distributed power generation as ‘an opportunity’ versus only 18% rating it as a ‘threat’.”
The Executive Summary sets out that “The growth of distributed generation and its threat to the power utility business model depends on technological developments and cost. Its rise in Europe has been subsidy-driven. Cost barriers remain in the way of it being truly market-driven. But, if these barriers can be overcome, they could set the scene for widespread global industry transformation. Many believe that point is within reach. Energy efficiency, falling solar prices, demand-side management and smart grid technology head the list of technological developments that the industry believes will have the biggest impact on their power markets.“
“At the moment we are beginning to come to the end of a phase where the spread of distributed generation has been policy and subsidy-led. With the economics of distributed generation fast changing, we are likely to move into a phase where take-up is commercially and market-led.” [p17]
The growth of smaller scale, localised distributed – or decentralised – energy generation technologies is critical in helping cities such as London determine their own energy future. Many of the larger scale centralised generation plant currently in operation reflected the opportunities that were available at the time: coal power stations were sited near coal-seams; the 1990s ‘dash for gas’ led to a dramatic increase of new ‘Combined Cycle Gas Turbine’ (CCGT) plants, often situated close to gas terminals. Increasingly, smaller, cleaner energy systems, from PV to CHP, heat pumps to district heating schemes, are becoming technologies of choice: importantly they are sited at the place of demand – where consumers actually need to use power and heat. It’s therefore good to see such significant support for this dramatic change in this timely and important analysis.
Shoreditch Heat Network Nominated for Green Award
September 2013: Hackney Homes has been nominated for an Inside Housing Green Performance Award for its recent refurbishment of the Shoreditch Heat Network. Further details on this scheme are provided on the following Vital Energi case study which describes how the company went about “replacing their ageing, inefficient and expensive gas and oil fired boilers with the London Borough of Hackney’s first council-owned Combined Heat and Power (CHP) plant and heat network“. Further details are also in the following article in the Hackney Post.
Hackney Homes set out that the network installed is “More energy efficient than traditional methods of generation, the combined heat and power engine burns natural gas to generate electricity and uses the heat generated to supply heating and hot water.
Residents will receive individual heat metering prepayment cards, giving them the freedom to manage and budget for their own heating; reducing the financial burden on households whose energy consumption is low.”
New VNEB District Heating Feasibility Study released
September 2013: Building on the November 2012 Vauxhall Nine Elms Battersea (VNEB) Energy Masterplan (7.8MB) (also see a previous post here on the earlier Opportunity Area Planning Framework for VNEB), a more detailed District Heating Feasibility Study has now been prepared for Wandsworth borough council and has been published online on the London Heat Map website.
The Nov 2012 study set out that the “Vauxhall Nine Elms Battersea Opportunity Area (VNEB OA) includes some of the highest density, large-scale development anywhere in London. As such, it offers huge potential for the development of a coherent, low carbon energy supply system.”
Key recommendations at the time included:
- To implement kick-start networks based around early loads in three locations, with routes identified as i. Lambeth ii. Central iii Battersea
- To continue dialogue with the new US Embassy development to show that a district energy network could be developed with benefits for the area and the Embassy.
- To open discussions to reinstate the hydraulic link to the Pimlico District Heating Undertaking Energy Centre – this is referring to a tunnel under the Thames which originally supplied waste heat from Battersea Power Station to the Pimlico District Heating system on the north side of the river (see more on this here and here).
Building on this the new 2013 District Heating Feasibility Study seeks to demonstrate the “commercial case both for individual developers and a centralised operator of a district heating network” examining opportunities for two potential heat network options “the developers’ non-networked approach (as expressed in individual site energy strategy documents)… Heat prices are then set to offer a fixed level of whole life cost benefit to developers connecting to the system. Second, the economic performance of heat delivery for the central scheme operator is demonstrated based on the heat prices identified from the developer perspective.”
Phasing of the build-out of the networks is considered alongwith an investment analysis of the different network options. Key to the recommendations sets out on page of the report is identifying a “project champion’ within the delivery vehicle to provide impetus and encouragement to the private sector to participate in the scheme”.
Posted in Decentralised Energy, Library, News
Tagged CHP, Community Heating, Decentralised Energy, Lambeth, Wandsworth
Leave a comment