Site search:
-
What’s new?
Energy for London Tags
Brent Buildings Camden Carbon Emissions CHP Cities Climate Adaptation Community Heating Community Initiatives Croydon Data DECC Decentralised Energy Distribution ECO Energy Costs Energy Efficiency Enfield FIT Fuel Poverty Funding Green Deal Hackney Haringey Housing Islington Lambeth Library Local Authorities Mayor Newham Ofgem Olympics Photovoltaics Planning RE:FIT RE:NEW Renewable Energy Retrofit Southwark Tower Hamlets Transport Waltham Forest Waste WestminsterEnergy Archives:
- February 2021 (1)
- January 2021 (15)
- December 2020 (15)
- November 2020 (9)
- October 2020 (3)
- August 2020 (5)
- July 2020 (3)
- June 2020 (4)
- April 2020 (10)
- March 2020 (5)
- February 2020 (2)
- January 2020 (3)
- October 2019 (1)
- September 2019 (4)
- August 2019 (2)
- July 2019 (1)
- August 2018 (1)
- November 2016 (8)
- October 2016 (8)
- September 2016 (2)
- August 2016 (8)
- July 2016 (14)
- April 2016 (12)
- March 2016 (16)
- February 2016 (8)
- January 2016 (4)
- December 2015 (1)
- November 2015 (1)
- October 2015 (16)
- September 2015 (3)
- June 2015 (1)
- May 2015 (1)
- April 2015 (1)
- March 2015 (1)
- February 2015 (1)
- January 2015 (1)
- December 2014 (18)
- November 2014 (4)
- August 2014 (8)
- July 2014 (7)
- June 2014 (25)
- May 2014 (8)
- April 2014 (4)
- March 2014 (12)
- February 2014 (7)
- January 2014 (13)
- December 2013 (11)
- November 2013 (15)
- October 2013 (15)
- September 2013 (18)
- August 2013 (5)
- July 2013 (20)
- June 2013 (33)
- May 2013 (8)
- April 2013 (16)
- March 2013 (25)
- February 2013 (14)
- January 2013 (20)
- December 2012 (23)
- November 2012 (23)
- October 2012 (25)
- September 2012 (14)
- July 2012 (12)
- June 2012 (43)
- May 2012 (20)
- April 2012 (8)
- March 2012 (40)
- February 2012 (39)
- January 2012 (40)
- December 2011 (22)
- November 2011 (40)
- October 2011 (33)
- September 2011 (48)
- August 2011 (40)
- July 2011 (58)
- June 2011 (41)
- May 2011 (80)
- April 2011 (38)
- March 2011 (33)
- February 2011 (25)
- January 2011 (24)
- December 2010 (3)
- November 2010 (7)
- October 2010 (6)
- September 2010 (7)
- August 2010 (1)
- July 2010 (2)
- June 2010 (4)
- May 2010 (1)
- March 2010 (3)
- February 2010 (3)
- December 2009 (5)
- November 2009 (2)
- October 2009 (3)
- July 2009 (3)
- June 2009 (1)
- April 2009 (1)
- March 2009 (1)
- February 2009 (1)
- January 2009 (1)
- December 2008 (2)
- October 2008 (1)
- September 2008 (1)
- July 2008 (1)
- March 2008 (2)
- January 2008 (2)
- October 2007 (1)
- September 2007 (3)
- July 2007 (1)
- March 2007 (1)
- February 2007 (3)
- November 2006 (3)
- August 2006 (1)
- February 2006 (1)
- May 2005 (1)
- February 2004 (1)
Library
Integrating Environmental Thinking to ‘Make a City Great’
October 2013: A recent report by McKinsey sets out that “By 2030, 60 percent of the world’s population will live in cities. That could mean great things for economic growth—if the cities handle their expansion wisely.” How to Make a City Great sets out how city leaders need to ‘Integrate Environmental Thinking’ into their economic decision-making – highlighting work already underway providing ‘green’ retrofits of existing buildings to developing entire green districts, with a summary provided of technologies deployed in such districts in various cities around the world.
City Power Play: 8 Ways Local Energy Policies Can Boost the Economy
October 2013: Really interesting new report by US-based organisation, the Institute for Local Self-Reliance, describing how “dozens of cities are boosting their local economies while dramatically reducing greenhouse gases“. City Power Play: 8 Practical Local Energy Policies to Boost the Economy provides case studies on various US cities which have used the following routes to help promote energy efficiency and renewables through the following actions:
- Municipal utilities
- Community choice aggregation
- Building energy codes
- Building energy use disclosure
- Local tax authority
- Solar mandates
- Permitting
- Local energy financing
A lot to learn from this excellent analysis, which can be downloaded here.
Cities & Biodiversity Report Released
 October 2013: A new study released by the UN Environment Programme focussing on how “Increasing urbanization over the next decades presents not only unprecedented challenges for humanity, but also opportunities to curb climate change, reduce water scarcity and improve food security, according to the world’s first global assessment on the relationship between urbanization and biodiversity loss” was released earlier this week in New York. The full news release can be read here. The study – Cities and Biodiversity Outlook – here. A short film – An Urbanising Planet – based on the study can be seen here.
October 2013: A new study released by the UN Environment Programme focussing on how “Increasing urbanization over the next decades presents not only unprecedented challenges for humanity, but also opportunities to curb climate change, reduce water scarcity and improve food security, according to the world’s first global assessment on the relationship between urbanization and biodiversity loss” was released earlier this week in New York. The full news release can be read here. The study – Cities and Biodiversity Outlook – here. A short film – An Urbanising Planet – based on the study can be seen here.
New VNEB District Heating Feasibility Study released
September 2013: Building on the November 2012 Vauxhall Nine Elms Battersea (VNEB) Energy Masterplan (7.8MB) (also see a previous post here on the earlier Opportunity Area Planning Framework for VNEB), a more detailed District Heating Feasibility Study has now been prepared for Wandsworth borough council and has been published online on the London Heat Map website.
The Nov 2012 study set out that the “Vauxhall Nine Elms Battersea Opportunity Area (VNEB OA) includes some of the highest density, large-scale development anywhere in London. As such, it offers huge potential for the development of a coherent, low carbon energy supply system.”
Key recommendations at the time included:
- To implement kick-start networks based around early loads in three locations, with routes identified as i. Lambeth ii. Central iii Battersea
- To continue dialogue with the new US Embassy development to show that a district energy network could be developed with benefits for the area and the Embassy.
- To open discussions to reinstate the hydraulic link to the Pimlico District Heating Undertaking Energy Centre – this is referring to a tunnel under the Thames which originally supplied waste heat from Battersea Power Station to the Pimlico District Heating system on the north side of the river (see more on this here and here).
Building on this the new 2013 District Heating Feasibility Study seeks to demonstrate the “commercial case both for individual developers and a centralised operator of a district heating network” examining opportunities for two potential heat network options “the developers’ non-networked approach (as expressed in individual site energy strategy documents)… Heat prices are then set to offer a fixed level of whole life cost benefit to developers connecting to the system. Second, the economic performance of heat delivery for the central scheme operator is demonstrated based on the heat prices identified from the developer perspective.”
Phasing of the build-out of the networks is considered alongwith an investment analysis of the different network options. Key to the recommendations sets out on page of the report is identifying a “project champion’ within the delivery vehicle to provide impetus and encouragement to the private sector to participate in the scheme”.
Posted in Decentralised Energy, Library, News
Tagged CHP, Community Heating, Decentralised Energy, Lambeth, Wandsworth
Leave a comment
London’s Zero Carbon Energy Resource
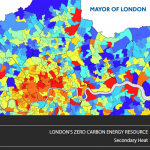 September 2013: Detailed GLA-commissioned study looking at “two particular categories of heat, both of which can be termed ‘secondary sources’: waste heat arising as a by-product of industrial and commercial activities; and the heat that exists naturally within the environment (air, ground, water).”
September 2013: Detailed GLA-commissioned study looking at “two particular categories of heat, both of which can be termed ‘secondary sources’: waste heat arising as a by-product of industrial and commercial activities; and the heat that exists naturally within the environment (air, ground, water).”
Details of the full report here (direct links below) the findings of which include:
- For most secondary heat sources, their temperature is too low for direct use. It is therefore necessary to ‘upgrade’ them to a useful temperature using heat pumps. Heat pump efficiency is important for secondary heat source utilisation as it affects the cost and carbon intensity of the heat delivered and will impact London’s electrical infrastructure.
- Analysis shows that by using heat pumps to deliver heat at 70°C, the total heat that could be delivered from secondary sources in London is of the order of 71 TWh/yr which is more than the city’s total estimated heat demand of 66 TWh/yr in 2010.
- The proportion of London’s heating demand that could be met by district heating networks operating at 70°C could rise to 30 TWh/yr by 2050, assuming ambitious retrofit programmes were implemented over that period.
Secondary Heat Study – Summary Report
Secondary Heat Study – Phase 1
Secondary Heat Study – Phase 2
Datasets for the study are available on the London Datastore
Posted in Decentralised Energy, Library, News
Tagged Community Heating, Decentralised Energy
Leave a comment
Draft London Sustainable Design Planning Guidance released
 September 2013: The Mayor has issued for public consultation draft supplementary planning guidance (SPG) on Sustainable Design and Construction, which sets out that all major planning applications for developments submitted to the GLA from 1 October 2013 will need to provide CO2 emission savings 40% beyond the 2010 building regulation requirements. This requirement was originally set out in the 2011 London Plan CO2 targets for residential and non-domestic buildings (Policy 5.2). The draft SPG is available here and the deadline for comments is 21 October 2013:
September 2013: The Mayor has issued for public consultation draft supplementary planning guidance (SPG) on Sustainable Design and Construction, which sets out that all major planning applications for developments submitted to the GLA from 1 October 2013 will need to provide CO2 emission savings 40% beyond the 2010 building regulation requirements. This requirement was originally set out in the 2011 London Plan CO2 targets for residential and non-domestic buildings (Policy 5.2). The draft SPG is available here and the deadline for comments is 21 October 2013:
The SPG adds to the London Plan climate and energy policies by providing additional detail on:
- Optimising the use of passive design measures and energy efficiency solutions to help reduce energy consumption
- Setting out minimum requirements for energy masterplans
- Connecting to an existing district heating scheme
- the use of CHP and onsite heat networks (and references that further information can be found in the ‘District Heating Manual for London‘)
Pages 49-50 provide some helpful detail on the use of CO2 off-set funds stating that“Boroughs may agree with a developer for the developer to directly off-set any shortfall in carbon dioxide reductions from a scheme by installing a carbon dioxide saving project off-site. Measures could include directly funding or installing community energy and retrofitting projects”. On the price of carbon, the SPG says “Boroughs should develop and publish a price for carbon dioxide” – but goes on to provide an example of using the Zero Carbon Hub’s suggested price of £46 per tonne:
” The overall contribution should be calculated over 30 years. For example,using the Zero Carbon Hub price equates to £46 x 30 years = £1,380 per tonne of carbon dioxide to be off-set.”
The guidance goes on to say: “It is essential that boroughs identify a suitable range of projects that can be funded through the carbon dioxide off-set fund. Preference should be given to retrofitting publicly owned property as this would provide wider community benefit. Initial discussions suggest that schools, council buildings and social housing are the buildings that could be retrofit most readily. Another option could be establishing a borough wide revolving energy fund, where a loan is provided to local residents or businesses wanting to retrofit energy and water saving measures.” Islington have recently published details of their own carbon offset fund – with a buy-out price starting at £950 – details here.
Paras 2.4.64 include some interesting new information with guidance on incorporating the use of demand side response measures, stating that:
“When negotiating with developers on planning applications, boroughs should encourage them to install systems that would enable the development to take advantage of demand side response … The Mayor has set up a permanent working interface with UK Power Networks to identify initiatives that each might take to support the development of demand side response measures within the UKPN network.“
Mayor releases emission accounting guidance for the construction industry
September 2013: New GLA report – “The Construction Scope 3 (Embodied) Greenhouse Gas Accounting and Reporting Guidance is aimed at helping professionals working within the construction industry to better understand and account for the embodied greenhouse gas emissions associated with construction; for example, those emissions relating to the extraction of raw materials and manufacture and transport of products used in new build and refurbishments”.
This report was led by Best Foot Forward working in collaboration with the Greater London Authority and the London Sustainable Development Commission.
New London guidance on preparing planning energy assessments released
September 2013: In line with Policy 5.2 of the London Plan, all major new developments submitted for planning in London are required to provide a detailed energy assessment as part of their planning application. The GLA has provided developers with additional guidance setting out in detail on how these assessments should be undertaken and, as a result of new planning energy targets being proposed by the Mayor (see below), a revised energy assessment guidance document has just been released.
The guidance has been updated to align with the Mayor’s recent proposals, set out in a draft Supplementary Planning Guidance (SPG) document on sustainable design and construction, that states that from 1st of October 2013, the Mayor will apply the 40% carbon reduction target (beyond Part L 2010) to all planning applications. This target has been set to work to the Government’s long-standing commitment for all new homes to be zero carbon by 2016.
Things have however become more complicated in the past few weeks… The Department for Communities and Local Government (DCLG) has recently announced a step-back in carbon requirements in their new building regulations standards for England, which will now come into operation with a delayed start-date of April 2014. At the same time however, the Government has continued to state their continued commitment to the 2016 zero carbon target. The GLA’s guidance document attempts to address this with the following statement:
“At this stage the target will remain 40% beyond 2010 Building Regulations. Following the announcement regarding the proposed changes to Part L of the Building Regulations by the Department of Communities and Local Government on the 30th July 2013 along with any new modelling considerations the Mayor is reviewing the implications for new developments. A further update of this guidance will be issued, if necessary, to reflect the changes to Part L of the Building Regulations coming into effect on the 6 April 2014 and the conclusions of the Housing Standards Review. This update will also reflect any changes to the Supplementary Planning Guidance (SPG) on Sustainable Design and Construction arising following consultation.”
The recently released GLA monitoring report on the implementation of the London Plan’s energy policies clearly shows that the development industry can respond to challenging planning energy targets, and London is now seeing significant growth in climate-friendly buildings which are both highly energy efficient, and are also generating a proportion of their own heat and power needs through onsite decentralised energy generation technologies. At the same time, Government appears to be ignoring such evidence and is going backwards in its commitments on the development of low carbon buildings.
Latest review of implementation of London Plan energy policies
September 2013: The GLA have recently produced their latest update on how the energy and climate policies in London’s spatial planning strategy – the London Plan – have helped drive forward the development of lower carbon buildings in the capital. The new 2013 report – along with previous years studies – can be downloaded here. An earlier post here provides some details on these reports.
The study ‘Energy Planning: Monitoring the implementation of London Plan energy policies in 2012‘ provides an analysis of the energy assessments relating to all finalised (stage II) planning applications determined from 1 January to 31 December 2012. As the Executive Summary of the report sets out “London planning authorities must consult the Mayor on all planning applications that are of strategic importance to London . For each planning application referable to the Mayor, an energy assessment is required setting out how the development will meet the London Plan energy policies. Following the order of the Mayor’s energy hierarchy, each energy assessment is required to set out how the development will:
- Use less energy
- Supply energy efficiently
- Use renewable energy”
The analysis highlights how the London Plan’s policies are making significant headway in helping drive forward the development of more energy efficient, climate-friendly buildings in London. Some of the findings include:
- High levels of energy demand reduction achieved with developments exceeding the requirements of Building Regulations through energy efficiency alone. The associated investment of circa £32 million will help to reduce consumers’ energy bills.
- Circa £20 million of investment in new, high efficiency combined heat and power (CHP) plant able to produce 29MW of electricity and a similar amount of heat.
- 74MW of cumulative CHP electrical capacity has been secured through the planning process since 2010 to the end of 2012, broadly equivalent to the capacity required to supply 150,000 homes.
- Circa £133 million of investment in heat network infrastructure for approximately 53,000 communally heated dwellings
- Continued investment in on-site renewable energy systems, including approximately £16 million to provide circa 87,000m2 of photovoltaic solar panels.
Posted in Library, News
Tagged Buildings, CHP, Community Heating, Decentralised Energy, Energy Efficiency, Photovoltaics, Planning, Renewable Energy
Leave a comment
Poverty figures for London
September 2013: Recently released GLA research indicates that:
- The number of Londoners living in poverty has seen little change over the last few years.
- More than a third of London’s children are in households with income below the poverty line, though rates have again fallen. The poverty rate for children in London, after housing costs, remains higher than for any other region, but is at its lowest level for 16 years.
- Child poverty in Outer London, before housing costs are taken into account, has fallen to the same level it was when the Government set Child Poverty reduction targets.
Observing London: Weather data needed for London to thrive
17 July 2013: Lloyds news highlights a new report: “Thanks to a new initiative by the London Climate Change Partnership (LCCP) in partnership with the Met Office and Lloyd’s, London is set to improve how it collects and uses weather data across the capital.
The new report: Observing London: Weather data needed for London to thrive, details how the initiative will provide economic benefits in areas such as flood management, transportation and building design.”
Affinity Sutton report includes key findings for the Green Deal
July 2013: Housing group Affinity Sutton has issued the final research report – as part of their Future Fit project – which examines the actual energy savings achieved by 150 homes as a result of installing energy efficiency measures. It’s an excellent study with some key findings which will be of important consideration to policy-makers on programmes such as the Green Deal.
The report – FutureFit: Final Report – is downloadable here (and data report here). The conclusions include the following:
- A fabric first approach does work and residents,on the whole, have felt benefits from living in a retrofitted home.
- Identifying energy savings was challenging and there needs to be more transparent mechanisms to show energy usage in the home.
- Electricity use is unpredictable. Adding the GreenDeal charge to the electricity bill will make identifying savings even harder and could result in bad press for the policy.
- SAP is not an appropriate tool for a PAYS model and could result in negative consequences for three out of four Affinity Sutton residents if they were to take up the Green Deal.
The foreword to the report [p4] by Affinity Sutton’s CEO sets out why the organisation in not utilising the Green Deal at present:
“Very few studies of energy bills before and after retrofitting social housing are in the public domain. This report is a major step forward for the sector in showing how retrofitted properties actually perform and how residents find living with the effects. But it is very much a starting point from which much more investigation is required. And although the results make it clear why Affinity Sutton is not currently supporting the Green Deal in our homes, this report sets out why it is so important to find a way to make it work for the very people who need it most.”