Site search:
-
What’s new?
Energy for London Tags
Brent Buildings Camden Carbon Emissions CHP Cities Climate Adaptation Community Heating Community Initiatives Croydon Data DECC Decentralised Energy Distribution ECO Energy Costs Energy Efficiency Enfield FIT Fuel Poverty Funding Green Deal Hackney Haringey Housing Islington Lambeth Library Local Authorities Mayor Newham Ofgem Olympics Photovoltaics Planning RE:FIT RE:NEW Renewable Energy Retrofit Southwark Tower Hamlets Transport Waltham Forest Waste WestminsterEnergy Archives:
- February 2021 (1)
- January 2021 (15)
- December 2020 (15)
- November 2020 (9)
- October 2020 (3)
- August 2020 (5)
- July 2020 (3)
- June 2020 (4)
- April 2020 (10)
- March 2020 (5)
- February 2020 (2)
- January 2020 (3)
- October 2019 (1)
- September 2019 (4)
- August 2019 (2)
- July 2019 (1)
- August 2018 (1)
- November 2016 (8)
- October 2016 (8)
- September 2016 (2)
- August 2016 (8)
- July 2016 (14)
- April 2016 (12)
- March 2016 (16)
- February 2016 (8)
- January 2016 (4)
- December 2015 (1)
- November 2015 (1)
- October 2015 (16)
- September 2015 (3)
- June 2015 (1)
- May 2015 (1)
- April 2015 (1)
- March 2015 (1)
- February 2015 (1)
- January 2015 (1)
- December 2014 (18)
- November 2014 (4)
- August 2014 (8)
- July 2014 (7)
- June 2014 (25)
- May 2014 (8)
- April 2014 (4)
- March 2014 (12)
- February 2014 (7)
- January 2014 (13)
- December 2013 (11)
- November 2013 (15)
- October 2013 (15)
- September 2013 (18)
- August 2013 (5)
- July 2013 (20)
- June 2013 (33)
- May 2013 (8)
- April 2013 (16)
- March 2013 (25)
- February 2013 (14)
- January 2013 (20)
- December 2012 (23)
- November 2012 (23)
- October 2012 (25)
- September 2012 (14)
- July 2012 (12)
- June 2012 (43)
- May 2012 (20)
- April 2012 (8)
- March 2012 (40)
- February 2012 (39)
- January 2012 (40)
- December 2011 (22)
- November 2011 (40)
- October 2011 (33)
- September 2011 (48)
- August 2011 (40)
- July 2011 (58)
- June 2011 (41)
- May 2011 (80)
- April 2011 (38)
- March 2011 (33)
- February 2011 (25)
- January 2011 (24)
- December 2010 (3)
- November 2010 (7)
- October 2010 (6)
- September 2010 (7)
- August 2010 (1)
- July 2010 (2)
- June 2010 (4)
- May 2010 (1)
- March 2010 (3)
- February 2010 (3)
- December 2009 (5)
- November 2009 (2)
- October 2009 (3)
- July 2009 (3)
- June 2009 (1)
- April 2009 (1)
- March 2009 (1)
- February 2009 (1)
- January 2009 (1)
- December 2008 (2)
- October 2008 (1)
- September 2008 (1)
- July 2008 (1)
- March 2008 (2)
- January 2008 (2)
- October 2007 (1)
- September 2007 (3)
- July 2007 (1)
- March 2007 (1)
- February 2007 (3)
- November 2006 (3)
- August 2006 (1)
- February 2006 (1)
- May 2005 (1)
- February 2004 (1)
Library
Merton Rule comes in for criticism
July 2012: Established by Housing Minister Grant Schapps, the Local Housing Delivery Group recently published its review of planning and also local standards in new housing development. The news release sets out that “With the reduction in central planning guidance and the forthcoming abolition of regional housing targets, the role of local authorities in planning for new homes becomes even more critical and the new National Planning Policy Framework (NPPF) poses a challenge for them to develop Local Plans which are both sustainable and viable.”
The Group has produced an interim report: A Review of Local Standards for the Delivery of New Homes. It concludes that there is “significant scope for simplification of the standards regime and recommends an urgent Government-backed review and consolidation of existing local housing standards to ensure they meet the aspirations of local communities without undermining viability.”
As such, the report looks at four key areas of standards that apply to new housing, and have included in their consideration requirements related to energy. The Group have come out critical to the ‘Merton Rule’ and similar mechanisms established by local authorities to drive the use of renewable energy through planning, stating:
“The Merton Rule was the first local planning policy to set a requirement on renewable energy for certain types of new development. It was named after the London borough that established it in 2003.
The rule required any new residential development of more than 10 units, or any commercial building over 1,000 square metres, to generate at least 10% of its energy needs from on-site renewable energy equipment in order to reduce its reliance on the National Grid and to reduce its CO2 emissions. Compliance with the policy was required as a condition of planning consent.
About half of the UK’s local authorities introduced a Merton-type rule. It also became part of national planning guidance through PPS 22. However, the variations on the Rule have now become confusing:
- Sometimes the targets are expressed as a percentage of energy generated (measured in kW hours).
- Sometimes the targets are around a decrease in CO2 instead (measured in tonnes of CO2e). Some local planning authorities “expect” a developer to achieve a 10% reduction through use of micro-renewables, others “require” 20%reductions or more.
- There are frequently different thresholds for when the policy is required – often 1,000 square metres or 10 units, but sometimes no threshold.
- About half of all planning authorities have no policy on this issue at all.”
The 2004 London Plan (the Mayor’s spatial planning strategy for London) also had a similar type of renewable energy requirement for new development, but this has been amended over time to set instead carbon reduction targets for new development in line with the Government’s zero carbon target for new homes by 2016. Go to the www.zerocarbonhub.org for more information on the 2016 target and read an earlier post for details on the Mayor’s current planning and energy requirements. Further information on the London Plan, including links to earlier version of the Plan, can be found on its wikipedia page here.
Posted in Library, News
Tagged Housing, London Plan, Merton, Planning, Renewable Energy
Leave a comment
Sustainable, resource efficient cities – Making it happen
July 2012: The United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP) unveiled a new initiative that “aims to reduce pollution levels, improve resource efficiency and reduce infrastructure costs in cities across the world. Launched at the Rio+20 summit in Brazil, the Global Initiative for Resource-Efficient Cities will work with local and national governments, the private sector and civil society groups to promote energy efficient buildings, efficient water use, sustainable waste management and other activities.
“In a rapidly urbanizing world, cities are increasingly becoming the focus of international sustainability efforts. Up to 80 percent of the world population is expected to reside in cities by 2050. Today, urban areas account for 50 percent of all waste, generate 60-80 percent of all greenhouse gas emissions and consume 75 percent of natural resources, yet occupy only 3 percent of the Earth’s surface.”
Download ‘Sustainable Resource Efficient Cities – Making it Happen’ here.
Posted in Library
Leave a comment
Exploring the Role of Cities and Buildings in the Green Economy
July 2012: A short paper produced by the US Green Building Council (USGBC), and launced at the recent Rio+20 sustainable development conference, which captures conversations taken across the US on current barriers to improving the energy efficiency of buildings. The conclusions have many parallels to problems faced here in London and the UK, including issues such as low awareness of the potential of energy savings, financial barriers and regulatory hurdles. The paper can be downloaded here (scroll half way down linked page).
Seven climate change lessons from the cities of Europe
 June 2012: London’s programmes to help reduce the carbon impact of the city are included in a new Carbon Disclosure Project (CDP) and Accenture study. Seven climate change lessons from the cities of Europe examines seven actions that leading European cities are taking to manage climate change in their cities. Further details on an Accenture press release and the following BusinessGreen article.
June 2012: London’s programmes to help reduce the carbon impact of the city are included in a new Carbon Disclosure Project (CDP) and Accenture study. Seven climate change lessons from the cities of Europe examines seven actions that leading European cities are taking to manage climate change in their cities. Further details on an Accenture press release and the following BusinessGreen article.
Merton’s Low Carbon Zone report
June 2012: Merton have just published their final report detailing the work undertaken in the Wandle Valley Low Carbon Zone. The zone is an area in a small part of South Mitcham and was one of ten zones across London that were set up as part of the Mayor’s RE:CONNECT programme “to radically reduce CO2 emissions at community level using novel routes to engagement. The aim was to make a 20% cut in Carbon dioxide (CO2) emissions by March 2012 for the whole area.” Download the report here.
Sutton Zero Carbon Resources
June 2012: The results of a project undertaken to help define a zero carbon retrofit strategy for buildings within the suburb of Hackbridge in the London Borough of Sutton has recently been published. The project was undertaken by BioRegional, with funding from the Sainsbury’s Family Charitable Trusts’ Climate Change Collaboration and the three key outputs – the authors say – have been “designed to be replicable in other areas.We hope that you will find them useful for your own projects.”
The area based strategy for zero carbon buildings report seeks to determine:
- How many and what type of buildings would need to be retrofitted.
- What different approaches could be taken to retrofitting, e.g. energy efficiency, building integrated renewable energy technologies or district heating.
- What would be the cost and delivery plan for the preferred approach, which may encompass a range of technologies.
- To develop an approach for formulating a zero carbon strategy for an area that other organisations, such as Local Authorities, Housing Associations and community groups could adopt.
The Retrofitting District Heating Systems study interestingly found that “district heating (using a variety of heat sources) achieved considerably more carbon emission savings than the full traditional retrofit option (whereby a building’s energy efficiency is improved by improving the building fabric and installing energy efficient or renewable sources of heat and electricity in the building itself) and at a lower cost.” A heat map for Hackbridge has also been produced.
And finally, an Energy retrofit tool for buildings spreadsheet tool which allows users to “input information about the domestic building stock in your area and the tool will then help decide on the best approach to retrofitting it using an area-wide approach.”
Posted in Library, News
Tagged Community Heating, Community Initiatives, Decentralised Energy, Heat Maps, Retrofit, Sutton
Leave a comment
Factsheet on Energy Bills
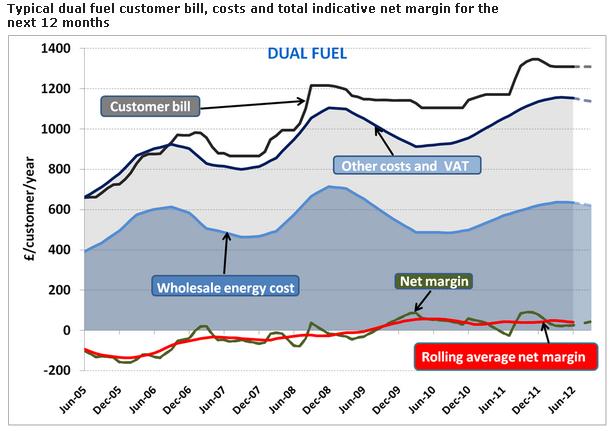
June 2012: Ofgem factsheet providing a useful update and breakdown of what makes up an average energy bill.
Information in relation to the ‘supplier margin’ – that is the profit made by energy customers per customer made across different fuel types – is also published on a regular basis by Ofgem in their ‘Electricity and Gas Supply Market Indicators‘ paper. This highlights that Ofgem’s “estimates also show that for the 12 month period from June 2012 up to and including May 2013 the total indicative net margin for a typical, standard tariff dual fuel customer will be approximately £30 per customer.”
External Insulation for London Semis
June 2012: South Kenton and Preston Park Residents Association (SKPPRA) recently obtained a grant from the Local Energy Assessment Fund (LEAF) to externally insulate a pair of semi-detached houses on the estate to show residents how this will make the houses warmer and easier to heat. Under the ‘warmhouse’ project two houses in Wembley were clad in external wall insulation and a series of detailed reports of the project have been published and are available to download from the ‘warmhouse’ website, which will provide some valuable learning for the roll out of the Green Deal in London.
Some points of interest:
- Detailed photographic records of the retrofit are posted in the first document, setting out the level of work undertaken to externally insulate these two homes.
- The second report provides a useful ‘scope of works’ document, which sets out the requirements of the insulation project to the contractor – a helpful template to any other similar project being considered.
- The fourth report highlights that, via a survey of local residents applying for to have their homes insulated, annual gas bills are shown to range from just over £400 to just under £1400 (presumably down to occupation levels rather than energy efficiency levels of the various homes?) with the majority of gas bills between £850 to £1100.
- The average annual gas consumption across residents submitting information is 21,500kWh of gas (hot water and space heating)
- Actual energy consumption modelling over the year hasn’t been undertaken(the project timeline most didn’t allow for this) and page 33 of this fourth report sets out a modelled indicative spread of space heating (only) consumption over the year
- Page 34 of the report then provides an indicative idea of how space heating consumption will be reduced as a result of the using external insulating walls, suggesting a >50% reduction in energy use in the home
- However, the FAQs set out however that “Utility bills and monthly gas readings will be required after the work is done so that the effect of the insulation on your energy consumption is recorded. As part of the preparation work a forecast will be made of the effect of the insulation on your heating energy consumption and the monthly gas readings will help to assess the accuracy of the forecast computer model.”
- Unfortunately, the project will not undertake a full fabric approach, the FAQs saying “No your windows will not be replaced – the grant is for the external insulation only”, but it’s possible the homes were already double-glazed…? However, it’s not immediately clear if this is the case with the two homes insulated
- Both external (and internal) wall insulation – and also replacement glazing (see Annex 1 of the Government’s recent response to the Green Deal and ECO consultation on the full list of qualifying measures) – will be subsidised under the forthcoming £1.3 bn a year Energy Company Obligation (ECO) scheme, which starts in October 2012
- It will be interesting to see how the houses perform in their new insulated state, and hence post-occupancy evaluation reports from the project will be of great value.
Posted in Library, News
Tagged Brent, Community Initiatives, Green Deal, insulation, Solid Wall Insulation, Wembley
Leave a comment
Planning and the Green Deal
June 2012: Thinktank Future of London has added a further helpful contribution to the issue of introducing the Green Deal in London, with a short paper, building on their recent report ‘Delivering Energy Efficiency in London, highlghting how planning will have a role to the success of the Green Deal.
A number of interesting points are raised including:
- There are around 600,000 homes in conservation areas in London, roughly half the national total (reference cited in paper here)- which will potentially be a significant issue for the mass role out of Solid Wall Insulation (SWI) – a key technology promoted by the forthcoming Green Deal and te £1.3 bn Energy Company Obligation (ECO)…
- …and around 60 per cent of all homes in the capital are solid wall
Download the paper ‘The Green Deal in London: Planning Q+A
Posted in Library, News
Tagged Energy Efficiency, Green Deal, insulation, Planning, Solid Wall Insulation
Leave a comment
Mass-retrofitting of a low carbon zone
June 2012 A very detailed piece of analysis undertaken by researchers at Edinburgh University (and published in the June issue of academic journal Energy Policy) which studies the work being undertaken in Sutton on adopting an area wide retrofit scheme in Hackbridge.
The conclusions highlight some really interesting findings relating to Hackbridge which are also very relevant to other areas of London. These include:
- housing built pre-1918 on average consumes 56% more energy and emits 41% more CO2 than houses built post-2001;
- the older housing stock is the worst performer in terms of energy efficiency; the most laborious and costly to improve;
- within the regeneration footprint, this type of housing makes up less than 20% of the housing stock. Nearly 40% of the housing stock having been built post-1970 is already benefitting from many of the measures proposed to save energy and reduce carbon emissions;
- almost one third of Hackbridge residents live in areas which rank within the top 25% most income-deprived in England, renting their homes from the Local Authority, Registered Social Landlords, Housing Associations or the private-rented sector. Homes in the social-rented sector that have been shown to consume less energy and to emit less CO2 than other housing types of a similar age in Hackbridge. Indeed, using the Government’s Standard Assessment Procedure for the energy rating of dwellings (SAP), the local authority housing in question is shown to out-perform the national average ratings across all dwelling types.
The study also includes: “…while policy analysis over the past decade has done much to highlight the potential contribution mass retrofits in the housing sector can make to reduce the rates of energy consumption and levels of carbon emissions, they also serve to illustrate how little is currently known about the institutional arrangements towns and cities are currently putting in place as integrated solutions to the problems climate change pose.“
Unusually for Energy Policy, the article full downloadable free of charge here.
Mayor to encourage community energy projects
June 2012: The Mayor has published revised ‘early minor alterations to the London Plan’ aimed at ensuring that the London Plan is fully consistent with the Government’s National Planning Policy Framework (published March 2012).
Page 30 of the ‘Early Minor Alterations’ document sets out a proposed revision to Chapter 5 of the London Plan – which addresses planning and climate change – to support community-led initiatives renewable and low carbon projects through neighbourhood planning. The exact amended text (in bold) follows below:
5.41 The Mayor’s supplementary planning guidance will set out broad guidelines to assist boroughs and, where appropriate,neighbourhoods, to define locations where stand-alone renewable energy schemes would be appropriate. The increased use of renewable heat will also significantly depend on the growth of heat networks. The Mayor and Boroughs will also encourage community-led initiatives for renewables and low carbon energy and examine how they can be supported through neighbourhood planning.” [page 30]
The supplementary planning guidance referred to is on renewable energy (which is also referred to in para 5.40 of Chapter 5 – see link above) and has, as yet, not been published by the Mayor. A major renewable energy study for London has however been completed and was issued in January 2012.
Further information to the background on new neighbourhood plans can be viewed here.
Posted in Library, News
Tagged Community Initiatives, Mayor, Planning, Renewable Energy
Leave a comment
FIT FAQ
June 2012: Confused by all the recent changes to the Government’s FIT programme? Here’s a FAQ document DECC have just posted online which goes some way to help explain…