Site search:
-
What’s new?
Energy for London Tags
Brent Buildings Camden Carbon Emissions CHP Cities Climate Adaptation Community Heating Community Initiatives Croydon Data DECC Decentralised Energy Distribution ECO Energy Costs Energy Efficiency Enfield FIT Fuel Poverty Funding Green Deal Hackney Haringey Housing Islington Lambeth Library Local Authorities Mayor Newham Ofgem Olympics Photovoltaics Planning RE:FIT RE:NEW Renewable Energy Retrofit Southwark Tower Hamlets Transport Waltham Forest Waste WestminsterEnergy Archives:
- February 2021 (1)
- January 2021 (15)
- December 2020 (15)
- November 2020 (9)
- October 2020 (3)
- August 2020 (5)
- July 2020 (3)
- June 2020 (4)
- April 2020 (10)
- March 2020 (5)
- February 2020 (2)
- January 2020 (3)
- October 2019 (1)
- September 2019 (4)
- August 2019 (2)
- July 2019 (1)
- August 2018 (1)
- November 2016 (8)
- October 2016 (8)
- September 2016 (2)
- August 2016 (8)
- July 2016 (14)
- April 2016 (12)
- March 2016 (16)
- February 2016 (8)
- January 2016 (4)
- December 2015 (1)
- November 2015 (1)
- October 2015 (16)
- September 2015 (3)
- June 2015 (1)
- May 2015 (1)
- April 2015 (1)
- March 2015 (1)
- February 2015 (1)
- January 2015 (1)
- December 2014 (18)
- November 2014 (4)
- August 2014 (8)
- July 2014 (7)
- June 2014 (25)
- May 2014 (8)
- April 2014 (4)
- March 2014 (12)
- February 2014 (7)
- January 2014 (13)
- December 2013 (11)
- November 2013 (15)
- October 2013 (15)
- September 2013 (18)
- August 2013 (5)
- July 2013 (20)
- June 2013 (33)
- May 2013 (8)
- April 2013 (16)
- March 2013 (25)
- February 2013 (14)
- January 2013 (20)
- December 2012 (23)
- November 2012 (23)
- October 2012 (25)
- September 2012 (14)
- July 2012 (12)
- June 2012 (43)
- May 2012 (20)
- April 2012 (8)
- March 2012 (40)
- February 2012 (39)
- January 2012 (40)
- December 2011 (22)
- November 2011 (40)
- October 2011 (33)
- September 2011 (48)
- August 2011 (40)
- July 2011 (58)
- June 2011 (41)
- May 2011 (80)
- April 2011 (38)
- March 2011 (33)
- February 2011 (25)
- January 2011 (24)
- December 2010 (3)
- November 2010 (7)
- October 2010 (6)
- September 2010 (7)
- August 2010 (1)
- July 2010 (2)
- June 2010 (4)
- May 2010 (1)
- March 2010 (3)
- February 2010 (3)
- December 2009 (5)
- November 2009 (2)
- October 2009 (3)
- July 2009 (3)
- June 2009 (1)
- April 2009 (1)
- March 2009 (1)
- February 2009 (1)
- January 2009 (1)
- December 2008 (2)
- October 2008 (1)
- September 2008 (1)
- July 2008 (1)
- March 2008 (2)
- January 2008 (2)
- October 2007 (1)
- September 2007 (3)
- July 2007 (1)
- March 2007 (1)
- February 2007 (3)
- November 2006 (3)
- August 2006 (1)
- February 2006 (1)
- May 2005 (1)
- February 2004 (1)
News
Funding Energy Efficiency Retrofit in London
November 2013: The GLA’s RE:NEW team have recently produced a guide identifying “potential sources of funding and finance available to London Boroughs, Registered Providers of Social Housing, private landlords and individuals to pay for energy efficiency retrofit measures in their housing.”
The sources of funding covered include the ECO, London Energy Efficiency Fund (LEEF) and the Social Housing Fund. Download the guide here.
Posted in Energy Efficiency, News
Tagged Energy Efficiency, Funding, Housing, London Green Fund, RE:NEW
Leave a comment
Reducing building CO2 emissions through better design
November 2013: The GLA have commissioned research to determine the “most effective way for buildings to reduce their carbon dioxide emissions through the design and fabric, based on the Building Regulations modelling tools.” This study will support the GLA’s recent Supplementary Planning Guidance on Sustainable Design & Construction guidance (for more of which here) and London Plan targets which requires all major planning applications from 1 October 2013 will need to provide CO2 emission savings 40% beyond the 2010 building regulation requirements.
Full details of the commission here.
Posted in Energy Efficiency, News
Tagged Buildings, Carbon Emissions, Energy Efficiency, Planning
Leave a comment
Potential for biodiesel from use cooking oil and FOGs in London
November 2013: The Mayor announced today that TfL will be deploying 12o buses from the Barking depot which will run on a blend of 80 per cent regular diesel and 20 per cent biodiesel. The press release states that “Biodiesel is a renewable, clean-burning fuel made from used cooking oil from the catering industry and tallow which is a residue from the meat processing trade. It is estimated that buses running on biodiesel produce 15 per cent less ‘well to wheel’ carbon emissions than an ordinary diesel-powered bus…No mechanical change is needed to allow a bus to run on a 20% blend of biofuel. The biodiesel in this trial is being supplied by Argent Energy with the standard diesel supplied by Prax Petroleum.”
The GLA also commissioned consultants LRS to produce a report on the market opportunity for a biodiesel market in London using used cooking oil (UCOs), fats oils and grease (FOGs) from commercial and domestic sources in the capital. The report can be downloaded here and sets out to “evaluate the potential to reduce the emissions and carbon footprint of the bus fleet in London by using up to B30 biodiesel instead of petrodiesel. Additional sustainability benefits would be achieved by using biodiesel made from used cooking oil (UCO) and fats, oils and greases (FOGs) instead of virgin oils.”
The report references recent disputes in London over UCO (see Daily Telegraph story here) stating “only 3-4 years ago illegal disposal of UCO down drains was recognised to be a significant issue, recently the demand for UCO has soared and led to ‘Cooking Oil Wars’, whereby collectors pay increasingly escalating prices to commercial organisations for UCO.”
In terms of London’s potential to produce biodiesel, on the basis of national estimates, the report suggests that using the “ratio of London’s population to the national population and uplifting to reflect the greater concentration of catering establishments in London gives an estimate of 32-44 million litres of UCO waste arisings in the London area. There are nearly 24,000 food and beverage service activities in London, along with a further 835 businesses in London working in the food manufacturing sector, most of which contribute to the production of UCOs. In particular London has over 8,000 fast food outlets, with some of the highest concentrations of such food outlets in the country.”
Lot of interesting findings in this comprehensive report. More on biodiesel use in London here.
Developing Heat Networks in London
November 2013: At the BRE’s recent event Developing heat networks in the UK three presentations were delivered on developments in London – links to which follow below:
Bunhill Heat and Power – Charlotte Large, Decentralised Energy Programme Manager, Islington Council
Identifying secondary heat sources for future sustainable heat networks – Peter North, Senior Manager – Programme Delivery (Sustainable Energy), GLA
The third presentation by Ian Smith, Head of Sustainable Services, Southwark Council, on London’s first energy from waste district heating network, can be found here.
Posted in Decentralised Energy, News
Tagged CHP, Community Heating, Decentralised Energy, Islington, SELCHP, Southwark, Waste
Leave a comment
Designing with data: shaping our future cities
 November 2013: A new report undertaken by ARUP for RIBA sets out that we are now at the “Dawn of a ‘smart era [where the] vast quantities of data we produce is set to revolutionise the way we design and build our cities”. A series of case studies are set out in ‘Designing with data: shaping our future cities‘ which includes the London Heat Map:
November 2013: A new report undertaken by ARUP for RIBA sets out that we are now at the “Dawn of a ‘smart era [where the] vast quantities of data we produce is set to revolutionise the way we design and build our cities”. A series of case studies are set out in ‘Designing with data: shaping our future cities‘ which includes the London Heat Map:
“One of the key benefits of adopting a smart approach to data is the ability to see lots of datasets in context with each other, and to detect temporal and spatial patterns. This transparency saves time and cost by reducing the time needed to find and process key data. The London Heat Map is a case in point. The interactive tool developed by the Greater London Authority (GLA) allows people to identify opportunities for Decentralised Energy projects in London, such as Combined Heat and Power (CHP) or district heating networks. Public organisations, property developers, social landlords or investors can also use it to view spatial information that can help them identify and develop Distributed Energy opportunities, such as data on: major energy consumers, fuel consumption and carbon emissions,energy supply plants, community heating networks,and heat density. The London Heat Map will evolve overtime alongside the Decentralised Energy for London programme and become more useful and sophisticated as boroughs and other stakeholders start inputting more energy data into the map.”
The report goes on to quote Alan Shingler, Partner, Head of Sustainability, Sheppard Robson who states “smart data could help test the impact of likely building fabric improvements through the Government’s Green Deal or regeneration schemes, to show how the GLA’s Heat Map would adjust to these variables. The data could also be used to model the impact of new renewable energy generation and future development on the map. This would enable the creation of a resilient low carbon transition plan for London that would take into account a range of considerations….where Combined Heat and Power (CHP) is proposed, heat could be more freely shared with neighbouring residential developments, schools, or public buildings with a relatively high heat load.“
Three recommendations are made in the report including one Energy for London strongly supports which is the greater ‘Digitisation the of the planning process’ where “Government should scope how it can standardise the digitisation of all information submitted for planning, and of standardising design data collection across local authorities. This public data should be open to unleash economic growth; and local authorities should be encouraged to use open data to inform local planning strategies.”
Posted in Decentralised Energy, News
Tagged Decentralised Energy, Heat Maps, London Heat Map, Planning
Leave a comment
GLA responds to Heat Enquiry
November 2013: The House of Commons Energy and Climate Change Select Committee is currently undertaking an enquiry into Heat. The terms of reference to the enquiry states that “so far much of government’s energy policy focus has been on low-carbon electricity generation (in particular, the Energy Bill, which aims to reform the electricity market). Yet heat is responsible for 46% of UK energy use, approximately a third of UK greenhouse gas emissions, and is a major cost in both the domestic and non-domestic sectors.”
The Greater London Authority (GLA) has submitted written evidence to the Committee outlining the significant decentralised energy programme underway in the capital. The evidence sets out a number of interesting points related to the wider scale deployment of heat networks as well as recommendations to Government in terms of its policies to promote decentralised generation. These include:
- The Mayor welcomes the Committee’s scrutiny of this often over-looked area of energy policy
- There are “inconsistencies in government’s energy policy and regulatory regime that are preventing heat generation and distribution in cities” which “…distort the market for heat by providing external financial support for some technologies, while largely ignoring heat networks“.
- Heat network deployment at the scale envisaged for London represents a significant infrastructural challenge, requiring approximately 3,600km of heat networks to be constructed by 2030 and equates to an investment opportunity of approximately £6bn
- Whilst district heating schemes can qualify for funding under ECO, the current two year target as well as uncertainty regarding longer-term target discourage energy suppliers from investing in these schemes. Government should consider setting longer term targets for the next phases of ECO, or provide guidance on how investment in district heating schemes can contribute to current or future targets
- We estimate that London housing development will generate at the very least £25m per annum under the proposed Allowable Solutions regime – by far the greatest amount of any region. Yet, because measures are likely to be cheaper outside London, London businesses and households will again be subsidising other regions and receiving less investment into low carbon, heating bill reducing measures. In addition, as Allowable Solutions investment is likely to lever ECO investment, there is a risk that the proposed scheme will exacerbate the imbalance in ECO investment away from London.
The Committee’s evidence gathering process continues in November – more of which can be found here.
The Big London Energy Switch
November 2013: London Councils’ Transport & Environment Committee recently discussed its initiative ‘The Big London Energy Switch‘ (further background to which is posted here). There have been two previous auctions through the collective energy switching scheme earlier this year, in April and June, and the initiative is now open to registration to users for a further auction to take place on 19 November. The London Councils’ paper highlights that a total of 1,847 residents switched through the first auction, saving on average £114 on their annual fuel bill.
Two more boroughs are now participating in this switch, bringing the total to 23. The note highlights some findings from the evaluation of the programme, undertaken by the Energy Saving Trust, stating:
- The scheme was effective at engaging with vulnerable residents, as evidenced by the high proportion of vulnerable residents that signed up, compared to the average proportions in London’s population – 41 per cent of those that registered their interest in the scheme indicated that they receive benefits.
- The tariffs offered from the energy companies for the spring auction were not attractive enough to persuade the expected proportion of registrants to make the switch – only 9 per cent of full registrants actually switched.
The note also highlights that the auction was originally set to take place in October however – “following discussions with energy suppliers, the date of the auction would be pushed back to 19 November… The reason is that there have been delays in Ofgem and the energy suppliers reaching consensus to implement the Retail Market Review (RMR) reforms, which are designed to make the market simpler and fairer for consumers.”
“Whilst changing the auction date is inconvenient for boroughs who have already publicised the date, the change increases the likelihood of energy suppliers providing bespoke tariffs in the auction and potentially increasing savings for the majority of residents.
“Overall we are disappointed that the date of the auction has been pushed back by a month, but hope that this will mean cheaper tariffs are offered by energy suppliers at auction and that more residents will be able to benefit from the scheme.”
The full EST evaluation report of the Big London Energy Switch, which includes 31 recommendations, can be downloaded here.
Energy & Climate Questions to the Mayor
October 2013: This month the Mayor has been asked questions in relation to:
Climate change leadership; London’s successful ‘green economy”;
potential for wind energy in London; the human contribution to climate change; Nissan Electric taxis‘; emissions from electric vehicles; promoting community energy through planning; Mayor’s briefing to the House of Lords on the Energy Bill; Mayoral visits to the Dagenham wind power project; RE:NEW programme advice on supplier switching; supplier switching advice; Nuclear power and London; bills savings achieved by households under RE:NEW; the Mayor’s energy advisor’s visit to New York; the Mayor’s energy advisor’s visit to Rio de Janeiro; the Mayor’s view on wind farms; London Energy Efficiency Fund (LEEF) Advisory Committee papers; nuclear power value to Londoners; roll-over energy contracts for SMEs; CO2 savings achieved under RE:NEW; the Mayor’s energy advisor’s visit to San Francisco; the Mayor’s view on MASDAR’s investment in the London Array; the Mayor’s view on shale gas; investment opportunities for London through financing wind power projects; hosting a London ‘Climate Week‘; RE:NEW advice supplier switching; renewable electricity supply to the Tube; SOURCE London charging points; London’s need for more electricity substations; completion of Affordable Warmth and Health Action Plan; applications to the London Schools Hydrogen Challenge; budget allocated to the Mayor’s new Affordable Warmth and Health Action Plan; the Mayor’s new Affordable Warmth and Health Action Plan; Londoners supported through the Mayor’s Know Your Rights helpline; GLA officers working on the new Affordable Warmth and Health Action Plan; RE:NEW report backs; Benefit Entitlement Checks (BECs) under RE:NEW; carbon offsets for flights; key activities in the Mayor’s new Affordable Warmth and Health Action Plan; private sector funding leveraged by RE:NEW; targets under the Affordable Warmth and Health Action Plan; community level responses to heatwaves; disseminating research undertaken to date on how to cope with heatwaves and the health impacts of cold homes.
Previous months questions to the Mayor can be found here.
Rundown on CHP in London
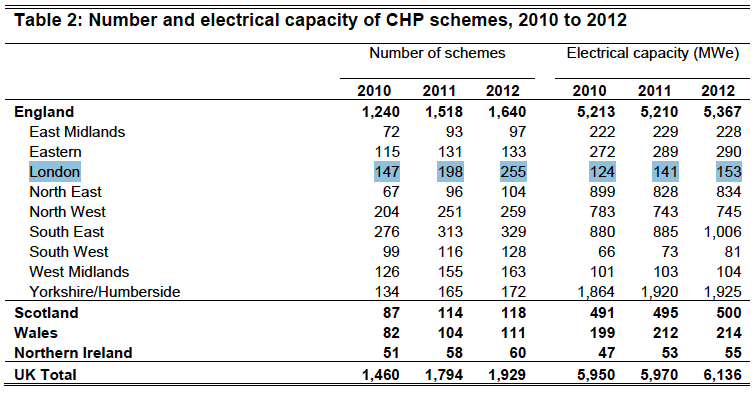
October 2013: Two recent sources issued by DECC provide data on the use uf Combined Heat and Power (CHP) plant in London. A useful article in DECC’s latest issue of Energy Trends provides a breakdown of CHP use in the regions, providing number of schemes, output, capacity installed and much more. Table 2 from the article is reproduced below.
The data shows a significant increase in the number of CHP schemes operating in London over the past two years (147 – 255) – a 73% jump – whilst generation capacity has grown by 29MW, reflecting the typically smaller scale nature (ie <1MWe) of CHP engines being installed in the capital. Of concern however is that Table 2B (below) from the article reveals that, though the capacity level of CHP has increased – the key metric – the output of decentralised lower-carbon heat and power in London – has actually fallen over the past two years. CHP electricity generation has fallen by 1% and heat generation by 2% in 2012 as compared to 2010 numbers. More promisingly however, the statistics indicate that the 2012 levels show a recovery a far steeper decline in output over the period 2010 to 2011 – so hopefully CHP is now ‘on the up’… Continue reading…
Licence Lite Update
October 2013: There has been little news recently on progress being made for the first ‘license lite’ license to be awarded – however – discussions do continue and below some recent references to the initiative are gathered together.
First, DECC’s Community Energy – Call for Evidence paper published in June 2013 covered the issue stating:
“96. Community renewable electricity projects typically sell their electricity through Power Purchase Agreements (PPAs), whereby an energy supply company agrees to buy electricity from a generator over a fixed period of time at a fixed rate. For community electricity generators it can be difficult to negotiate with large energy supply companies. Aggregators such as Smartest Energy have in the past helped community groups overcome this hurdle. We also recognise that the move from the Renewables Obligation to the Contracts for Difference (CfDs) is a significant one and that the structure of PPAs will need to change, to reflect the changes to the risk profile and the structure of CfDs. The Government has initiated a process to support the market in preparing for the CfD in order to speed this transition and reduce costs.
97. Another route to market for community-generated electricity is Licence Lite, a new form of electricity supply licence, which was proposed by Ofgem in February 2009. The purpose of the licence is to enable smaller scale electricity generators to overcome the costs, risks and complexities of operating in the electricity supply market. If successfully implemented, it will enable them to supply electricity into the retail electricity market and earn a higher market rate than at present for the power they produce.
98. Although no Licence Lite has yet been granted, initial applications have recently been made, including by the Mayor of London, through the Greater London Authority. We hope this will help resolve some of the issues around selling community-generated electricity, and we will be keen to see what evidence comes out of these cases.“
And two recent workshops also provided some information on the background to Licence Lite. At Ofgem’s community energy workshop held in September, Ofgem officials provided a short presentation on the basic benefits of being ‘License Lite’. And law firm Nabarro – who have undertaken significant work in this area for the GLA – held an event in July with a strong focus on licence lite where a helpful presentation was provided by the GLA providing information of their work to date and anticipated further actions. Some previous posts also go into further detail.
London’s secondary heat resource
October 2013: The GLA commissioned a detailed report earlier this year exploring opportunities in London to use high volumes of typically lower-temperature waste heat. Further details on this study – London’s Zero Carbon Energy Resource – can be downloaded here. And a recent presentation made at BRE’s ‘Developing heat networks in the UK ‘ also provides a good summary of some of the findings.
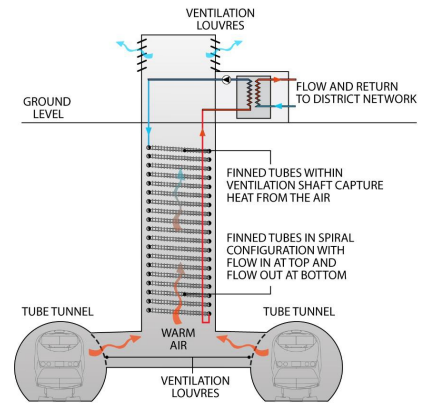
Heat is generated in London’s tube network as a result of trains braking, underground lighting and from passengers. This heat is rejected through ventilated shafts at strategic positions along the network at temperatures ranging typically from 12-29 degrees.
Most secondary heat sources need upgrading to higher temperatures to be useable in heat networks – this requires heat pumps. The minimum suitable temperatures for district heating is 55 degrees. Download the presentation ‘Secondary Heat – London’s Zero Carbon Energy Resource‘ here.
London’s ‘first EfW DH network’
October 2013: A presentation made at BRE’s recent ‘Developing heat networks in the UK ‘ provides a little background – and a few images – behind the new Southwark district energy network taking waste heat from the SELCHP energy from waste (EfW) plant and directing to five nearby housing estates -presentation here (and directly here). Further information on the following post here.
Posted in Decentralised Energy, News
Tagged Community Heating, Decentralised Energy, SELCHP, Southwark
Leave a comment