Site search:
-
What’s new?
Energy for London Tags
Brent Buildings Camden Carbon Emissions CHP Cities Climate Adaptation Community Heating Community Initiatives Croydon Data DECC Decentralised Energy Distribution ECO Energy Costs Energy Efficiency Enfield FIT Fuel Poverty Funding Green Deal Hackney Haringey Housing Islington Lambeth Library Local Authorities Mayor Newham Ofgem Olympics Photovoltaics Planning RE:FIT RE:NEW Renewable Energy Retrofit Southwark Tower Hamlets Transport Waltham Forest Waste WestminsterEnergy Archives:
- February 2021 (1)
- January 2021 (15)
- December 2020 (15)
- November 2020 (9)
- October 2020 (3)
- August 2020 (5)
- July 2020 (3)
- June 2020 (4)
- April 2020 (10)
- March 2020 (5)
- February 2020 (2)
- January 2020 (3)
- October 2019 (1)
- September 2019 (4)
- August 2019 (2)
- July 2019 (1)
- August 2018 (1)
- November 2016 (8)
- October 2016 (8)
- September 2016 (2)
- August 2016 (8)
- July 2016 (14)
- April 2016 (12)
- March 2016 (16)
- February 2016 (8)
- January 2016 (4)
- December 2015 (1)
- November 2015 (1)
- October 2015 (16)
- September 2015 (3)
- June 2015 (1)
- May 2015 (1)
- April 2015 (1)
- March 2015 (1)
- February 2015 (1)
- January 2015 (1)
- December 2014 (18)
- November 2014 (4)
- August 2014 (8)
- July 2014 (7)
- June 2014 (25)
- May 2014 (8)
- April 2014 (4)
- March 2014 (12)
- February 2014 (7)
- January 2014 (13)
- December 2013 (11)
- November 2013 (15)
- October 2013 (15)
- September 2013 (18)
- August 2013 (5)
- July 2013 (20)
- June 2013 (33)
- May 2013 (8)
- April 2013 (16)
- March 2013 (25)
- February 2013 (14)
- January 2013 (20)
- December 2012 (23)
- November 2012 (23)
- October 2012 (25)
- September 2012 (14)
- July 2012 (12)
- June 2012 (43)
- May 2012 (20)
- April 2012 (8)
- March 2012 (40)
- February 2012 (39)
- January 2012 (40)
- December 2011 (22)
- November 2011 (40)
- October 2011 (33)
- September 2011 (48)
- August 2011 (40)
- July 2011 (58)
- June 2011 (41)
- May 2011 (80)
- April 2011 (38)
- March 2011 (33)
- February 2011 (25)
- January 2011 (24)
- December 2010 (3)
- November 2010 (7)
- October 2010 (6)
- September 2010 (7)
- August 2010 (1)
- July 2010 (2)
- June 2010 (4)
- May 2010 (1)
- March 2010 (3)
- February 2010 (3)
- December 2009 (5)
- November 2009 (2)
- October 2009 (3)
- July 2009 (3)
- June 2009 (1)
- April 2009 (1)
- March 2009 (1)
- February 2009 (1)
- January 2009 (1)
- December 2008 (2)
- October 2008 (1)
- September 2008 (1)
- July 2008 (1)
- March 2008 (2)
- January 2008 (2)
- October 2007 (1)
- September 2007 (3)
- July 2007 (1)
- March 2007 (1)
- February 2007 (3)
- November 2006 (3)
- August 2006 (1)
- February 2006 (1)
- May 2005 (1)
- February 2004 (1)
Tag Archives: Anaerobic Digestion
‘London disposal authority calls for food waste ban’
5 October 2016: Let’s Recycle report on North London Waste Authority’s submission to the EFRA Select Committee inquiry into Food Waste in England with the NLWA stating that a: “ ban on commercial and industrial food waste to landfill would have the benefit of diverting industrial food wastes from disposal, including the quantity of food waste from small restaurants and shops, thus making food waste collections potentially more viable for these premises and potentially further stimulating the market for anaerobic digestion.”
The response goes on:
“However, it may have the unintended consequence of encouraging retailers to sell more short-life food to householders to avoid sending the food to relatively expensive AD and composting outlets; which would have to be guarded against.”
The NLWA response echoes recommendations made by the London Assembly Environment Committee in their Bag it or bin it?: Managing London’s domestic food waste.
Posted in News, Renewable Energy
Tagged Anaerobic Digestion, Renewable Energy, Waste
Leave a comment
Energy and Climate Questions to the Mayor
September 2013: This month the Mayor has been asked questions in relation to:
How the Mayor’s programmes will respond to the forthcoming IPCC’s (Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change) 5th Assessment Report; the Mayor’s “climate sceptic views“; London’s growing energy demand; £145k spend on climate change adaptation; the amount of energy generated from waste incineration; the number of GLA officers working on energy efficiency retrofit; the amount of ECO funding that could be directed to London; the operation of the RE:FIT schools energy efficiency programme in Harrow; the RE:FIT schools programme in Brent; Government’s proposed changes to building regulations and its potential impact on London Plan energy requirements; the Mayor’s response to DECC’s Community Energy – Call for Evidence; the Mayor’s support for community energy schemes in London – such as Brixton Energy; publication of the latest London Energy and Greenhouse Gas Inventory (LEGGI); the cost of producing ‘Using Local Powers to Maximise Energy Efficiency Retrofit – How to’ materials for London’? (report here); the terms of loans provided by the London Energy Efficiency Fund (LEEF); extending LEEF loans to the private sector; details of the LEEF Advisory Committee; consultancy companies working on LEEF; the amount spent by LEEF; the number of loans given out by LEEF; rollover energy contracts for SMEs; Londoners energy bills; the amount of renewable electricity provided by Source London electric vehicle charging points; funds previously spent on adding energy efficiency measures to Metropolitan Police buildings currently for sale; developing a Fuel Poverty Action Plan for London; the supply of electricity to London’s electric vehicle charging points; the supply of electricity to London Underground; London Green Deal targets; a London Green Roofs map; the Mayor’s Green Deal assessment on his home; stimulating Green Deal finance packages; spend of the Green Bus Fund; funding received from the Green Bus Fund; identifying brownfield land in London suitable for sustainable energy projects; CO2 savings achieved by the Mayor’s climate change programmes; potential for the London Pension Fund Authority to invest in low carbon energy projects; when the next update to the Mayor’s Climate Change Adaptation Strategy is to be published; how climate change will affect London’s summer temperatures; new anaerobic digestion plant in Surrey; the level of waste being directed to the Beddington incinerator; the London Plan’s policies on incineration; the Mayor’s approval of the Beddington incinerator; if the Mayor had pressed for the Beddington project to develop as a anaerobic digestion plant; if the Beddington incinerator can operate in combined heat and power (CHP) mode; heat network around the Beddington incinerator; the growth of waste incineration in London to 2016; the role for future incineration in London; local planning controls and fracking; the fracking potential in London; details of the new RE:NEW domestic energy efficiency programme; targets for the new RE:NEW programme; the choice of the Capita Group to manage the new RE:NEW programme; GLA buildings that have been treated by the RE:FIT programme; whether the Mayor’s Environment advisor had visited the Kings Cross CHP and district heating scheme.
Previous months questions to the Mayor can be found here.
Posted in Decentralised Energy, Energy Efficiency, News, Renewable Energy
Tagged Anaerobic Digestion, Brent, Buildings, Carbon Emissions, CHP, Climate Adaptation, Community Initiatives, Energy Security, Funding, Green Deal, Harrow, Lambeth, London Green Fund, Natural Gas, Planning, RE:FIT, RE:NEW, Retrofit, Schools, Transport, Waste
Leave a comment
A low carbon and more energy efficient West End needs to be prioritised
1 May 2013: The Financial Times today highlights concerns raised by London’s West End businesses on the reliability of electricity supply to the centre of the capital. Philippa Roe, leader of Westminster City Council, comments in the article that : “It is a real issue, not just for Westminster but for London. The problem is not generation, it’s distribution. It seems foolish not to be able to plan for our future energy needs.”
Issues related to climate and energy are set out in sections on infrastructure and the environment in a report published yesterday by the West End Commission. The report recognises the impact that climate change could have on businesses in the West End and sets out a number of significant changes to how lower carbon energy systems could be put in place to supply heat and power. These include:
- The transition to a low-carbon economy must also become one of the key objectives of the West End partnership, including coordinating underpinning programmes as they relate to retrofit of buildings, new energy and waste systems [para 23]
- The new West End partnership should also conduct an analysis to assess the appropriateness for the area of different forms of low carbon energy generation [para 24]
- Some early priorities are to… plan for a low carbon and more energy efficient West End [page 32]
- The development of new, high quality, energy efficient, mixed use/office space is a key factor in maintaining the West End’s ongoing economic competitiveness. [page 43]
- There is a concern amongst developers that the current approach to investment in the network must be improved if the West End is going to have a secure energy supply over the long-term. In its evidence the Westminster Property Association highlighted that ‘security and resilience of energy supplies area growing concern. This is an issue which goes to the heart of UK energy generation, distribution and regulation. The needs of the West End are quite exceptional, in national terms [page 43]
- The current regulatory system provides limited incentives for investment ahead of demand,creating uncertainty for developers and often additional cost if new power substations are needed to guarantee energy supply. Through their statutory spatial planning process and setting of a Community Infrastructure Levy, the boroughs have the mechanism to identify and prioritise infrastructure requirements. However, boroughs do not have the power to mandate investment in electricity infrastructure and electricity supply will only be improved if the regulator allows investment ahead of demand.The Commission believes that swift action should now be taken to implement a new approach to investment in energy supply ahead of demand that builds on the well-established body of evidence. Such an approach should include looking at greater use of innovative sources of energy supply such as the use of hydrogen fuel cells, block or district combined heat and power networks, anaerobic digestion and waste to energy. [page44]
- The report concludes that – In view of the pressing demand for a more resilient supply of energy to the West End,the new West End partnership should explore whether better use can be made of local decentralised and low carbon sources of supply such as district combined heat and power schemes, anaerobic digestion, energy from waste and hydrogen fuel cells, and whether more could be done to retrofit existing buildings to improve their energy efficiency and reduce demand. [page 46]
The West End Commission was convened by Westminster City Council in summer 2012 to review, explore and set out recommendations for the continued and future success of the West End of London.
Posted in Decentralised Energy, Energy Efficiency, News
Tagged Anaerobic Digestion, Camden, Decentralised Energy, Fuel Cells, Westminster
Leave a comment
Energy and Climate Questions to the Mayor
December 2012: This month the Mayor has been asked questions in relation to: the delay in the publication to the Mayor’s evaluation report of his home energy efficiency programme, RE:NEW; a response to the recent report that London experienced the largest increase in the number of Excess Winter Mortality of any region; the number of low carbon and renewable energy installations installed in fire stations currently threatened with closure; on the Mayor’s recent statement that the “energy policy of the country is in chaos“; the Deputy Mayor’s views on renewable energy; the representation of decentralised energy generators on the Mayor’s High Level Electricity Working Group; the Energy Bill and its support to the attainment of the Mayor’s 25 per cent decentralised energy target
Progress on the Mayor’s DE target; CHP capacity in London; TfL arrangements to secure electricity supply for the London Underground ; TfL energy costs; TfL procurement of electricity from London-based low carbon and renewable energy generators
progress being made under the London Energy Efficiency Fund (LEEF); the UK’s attractiveness to clean energy investment; discussions with energy companies over recent price hikes; a London target under the Energy Company Obligation (ECO)
job losses in the insulation industry in London; Mayor’s liaison with the Insulation Industry Forum; the slow take up under the Green Deal and the January launch of the Green Deal; London bid to the Green Deal Pioneer Places fund and here.
Energy efficiency improvements linked to home extensions and conversions; the 2018 energy efficiency requirement for the private rented sector (and here); that there will be no zero carbon homes developed on the Greenwich Peninsula; checks on the standard of work completed under the RE:NEW programme; future energy consumption related to London’s future population growth; the anticipated energy output from the 25 decentralised energy schemes currently being supported by the Mayor; funding directed to the Mayor’s decentralised energy programme; papers from future meetings of the Mayor’s High Level Electricity Working Group; and the potential for anaerobic digestion in London and the number of future AD plants in London.
Previous months questions to the Mayor can be found here.
Posted in News
Tagged Anaerobic Digestion, CHP, Decentralised Energy, Energy Efficiency, Fuel Poverty, Funding, Green Deal, RE:NEW, Renewable Energy
Leave a comment
Energy and Climate Questions to the Mayor
November 2012: This month the Mayor has been asked questions in relation to: the way the supplier obligation support for energy efficiency works and its shortfalls in terms of London; promotion of anaerobic digestion plants through the London Plan; how the GLA’s asset strategy can promote the low carbon economy; compensating for unavoidable carbon emissions during the Olympic Games; the Mayor’s view on the EU Emissions Trading Scheme (EUETS) and the international response to aviation being included in the EUETS.
Previous questions to the Mayor can be found here.
Posted in News
Tagged Anaerobic Digestion, Carbon Emissions, CERT, ECO, Green Deal, Olympics
Leave a comment
Renewable Electricity Generation in London begins to grow
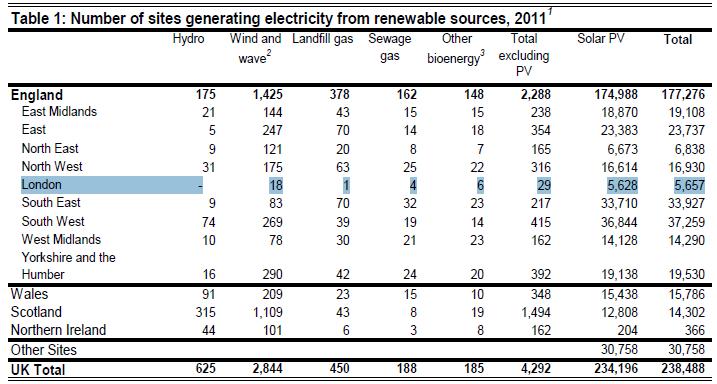
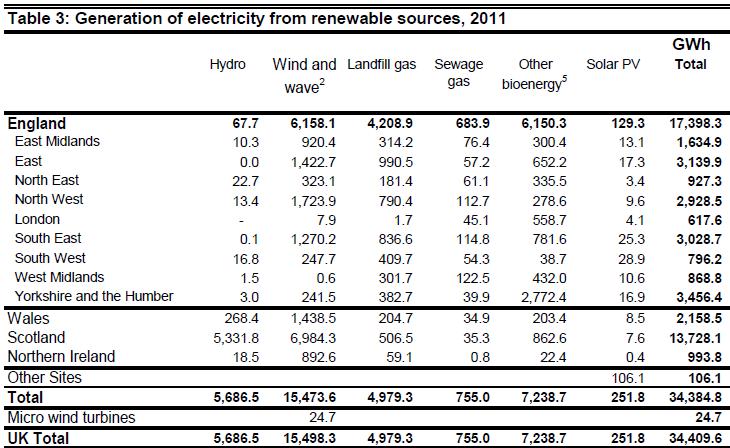
1 October 2012: DECC’s latest issue of Energy Trends includes new regional statistics on renewable electricity (not energy) generation. The article – Renewable electricity in Scotland, Wales, Northern Ireland and the regions of England in 2011– highlights (in Table 1) that 5,657 renewable electricity generating sites were operating in London as at the end of 2011. Not surprisingly the vast majority of these were photovoltaics (PV) – 99.48% to be precise – with a further 58 renewable technology schemes registered (this however compares with only 16 (non-PV) schemes as registered in last year’s statistics). The number of PV installations has risen more than fivefold compared to the number (1,044) in place at the end of 2010.
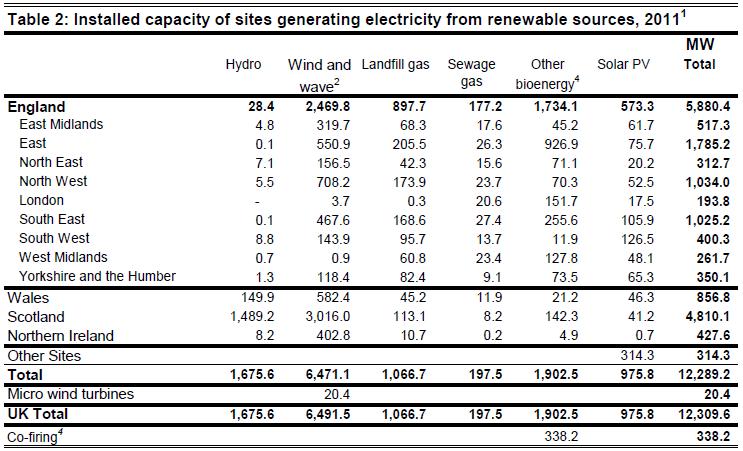
More importantly in terms of capacity and output, the following two tables (copied below) reveal that in 2011:
- London has 193.8 MW of electrical generating capacity (compared to 117.1 in 2010) – a 65% increase in renewable capacity over the year.
- PV capacity has risen six fold from 2.8 MW in 2010 to 17.5 MWas at the end of 2011
- However ‘Other biomass’ has seen the biggest overall increase in capacity – just over 40MW – over the year
- Oddly no sewage gas plants were registered in the 2010 statistics (a number of schemes have been operating in the capital for sometime…); it is now reported that 4 schemes operate in London to a total generating capacity of 20.6 MW.
- The ‘Wind and Wave’ category has increased by 8 in terms of installation numbers (10 to 18), however the capacity number remains the same – 3.7 MW – as of last year.
Following the level of overall renewable capacity added, there’s been a 60% increase in the amount of renewable electricity generated, rising from 385.7 GWh (gigawatt-hours) in 2010 to 617.6 GWh in 2011 (see table below).
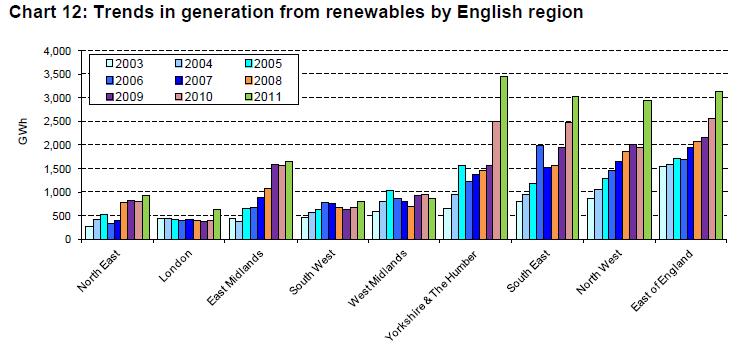
The article provides further analysis and comparisons of London’s output as compared to the rest of the English regions, which, as is already well documented, remains modest due to the limitations the capital has in exploiting key renewable technologies such as wind and landfill. Chart 12 in the article (copied below) however provides some cause for optimism as it illustrates that changes made to the national policy framework for renewables over the past few years- particularly with the advent of Feed in Tariffs (FITs) and Renewable Obligation (RO) Banding – is finally supporting London to take a small but positive step forward in terms of its renewable contribution, after several years of only limited progress.
Posted in News, Renewable Energy
Tagged Anaerobic Digestion, Data, Photovoltaics, Renewable Energy, Waste
Leave a comment
Food waste could provide London with new gas supply
January 2012: An article highlighting how Creative Health Lab, a social enterprise based in North London, are working towards developing a small scale, community Anaerobic Digestion (AD) project. AD projects in the UK at present are generally large, industrial scale technologies, but Creative Health Lab want to see the technology scaled down to a more local micro- level. The project LEAP project (the Local Energy Adventure Partnership) is currently looking at two North London sites where they can begin trialling the small-scale AD technology. Read the full article here.
Posted in News, Uncategorized
Tagged Anaerobic Digestion, Camden, Community Initiatives, Waste
Leave a comment
More challenging times for renewables in London?
21 October 2011: The Government’s proposals for future Renewable Obligation (RO) banding levels for different renewable electricity levels have been published today for consultation. The bands set the level of subsidy provided through granting Renewable Obligation Certificates (ROCs) – awarded per MWh (megawatt-hour) of electricity generated – and range from 0.5 ROCs to 2 ROCs per MWh depending on the technology. The ROCs programme runs in tandem to the Feed in Tariffs (FIT) mechanism but is applicable to larger renewable technologies, generally above 5MW capacity.
The consultation moves to providing longer term guidance on the levels of support available to renewable generators whilst also reducing the levels of ROCs support awarded to many technologies and also introducing an element of regression as in the FIT regime (ie a percentage reduction to the levels of support year on year).
Progress on developing larger renewable energy projects in London has been incredibly slow, with only a few notable schemes based around the use of sewage gas at water treatment plant, the capture of landfill gas, and single larger-scale wind project.
DECC’s proposals will do little to help and potentially much to hinder the situation for London. Key renewable technologies being supported for London such as advanced gasification and pyrolysis are to have their levels of support reduced (see Table 2 of the consultation paper for the full list of specific proposals). These are already high risk projects and hence this will do little to get these nascent technologies off the ground. Ditto for urban-based anaerobic digestion plant which are also having their levels of support reduced.
Similarly reducing support to energy from waste CHP without clarifying the level of Renewable Heat Incentive (RHI) tariff that might also be available will do little to inspire confidence in operators considering converting their plant to CHP mode and investing in new district heating infrastructure. Cities are already severely limited in their ability to contribute to the UK’s ambitious renewable energy targets: waste does however provide a key opportunity but project costs are typically much higher due to land value amongst many other factors.
More needs to be done to support the growth of renewables in London and other cities to exploit opportunities to deliver low carbon heat and power to their communities. Government should perhaps consider introducing a ‘ROC uplift’ for urban based schemes to help bring these more challenging city renewable schemes forward – that is – an additional 0.5 to 1.0 ROCs for those schemes developed in cities, with a priority given to those that deliver decentralised heat networks as part of their scheme.